Our Cancer and Immunomodulatory Peptide Libraries allow for hundreds of cancer-related peptides to be analyzed in parallel. This can drastically reduce the time needed for your drug discovery, ligand-binding, or antibody development efforts.
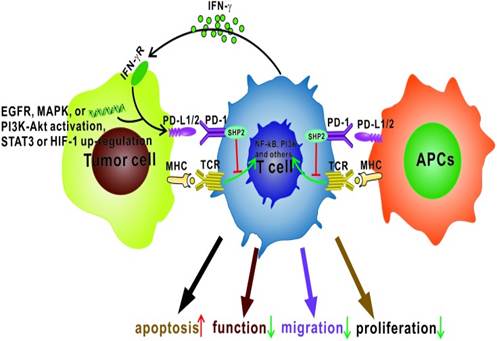
The effects of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)−programmed death 1/2 ligand (PD-L1/2) interaction on T cells. PD-L1/2 is expressed by tumor cells and antigen-presenting cells (APCs). In tumor cells, PD-L1 expression may be induced by interaction between IFN-γ and IFN-γ receptor (IFN-γ R), activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and/or PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, and upregulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) or hypoxia induced factor 1 (HIF-1). Then, interaction of PD-1 with PD-L1 can activate Src homology region 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 (SHP2) and inhibit activation of T cell receptor (TCR)/major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-triggered NF-κB, PI3K, or other signaling pathways, leading to increased apoptosis and impaired T cell function, migration, and proliferation.
Figure from: Song M et. Al. Future of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 applications: Combinations with other therapeutic regimens. Chin J Cancer Res. 2018 Apr; 30(2): 157–172. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.02.01
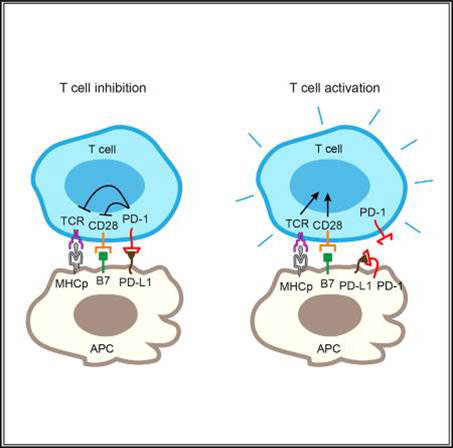
T cell inhibitory receptor PD-1 expressed on tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating APCs neutralizes its ligand, PD-L1, in cis to inhibit canonical PD-1 signaling.
The interaction between PD-1 on T cells and its ligand PD-L1, which is highly expressed on several types of human tumor cells and tumor infiltrating immune cells, restrains the activity of effector T cells against human cancers and chronic virus infections.
Zhao et al. (Cell Rep. 2018 Jul 10;24(2):379-390) show that the T cell inhibitory receptor PD-1 expressed on tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating APCs neutralizes its ligand, PD-L1, in cis to inhibit canonical PD-1 signaling. Selective blockade of tumor-intrinsic PD-1 frees up tumor PDL1 for T cell suppression. Peptide/protein that block PD-L1/PD-1 interactions have produced durable clinical benefits.

Social Network Confirmation